Alternative: Docker Compose Setup
Getting Started with Docker Compose
Install Docker Desktop or Docker Engine and Docker CLI with the Docker Compose Plugin (
docker composecommand).We DON’T support the usage of the Compose standalone binary (
docker-composecommand) as its installation method is no longer supported by Docker.We recommend the latest version of Docker Desktop or Docker Engine and Docker CLI with Docker Compose Plugin. The minimum version for Docker Compose is 1.27.0+ as of this version the latest Compose file format is supported.
Hint
Make sure that Docker Desktop has enough memory (~ 6GB). To adapt it, go to
Settings -> Resources.Check that all local network ports used by Docker Compose are free (e.g. you haven’t started a local MySQL server when you would like to start a Docker Compose instance of mysql)
Run
docker compose pull && docker compose upin the directorydocker/Open the Artemis instance in your browser at https://localhost
Run
docker compose downin the directorydocker/to stop and remove the docker containers
Tip
docker compose pull command is just necessary the first time as an extra step;
otherwise, Artemis will be built from source as you don’t already have an Artemis Image locally.Other Docker Compose Setups
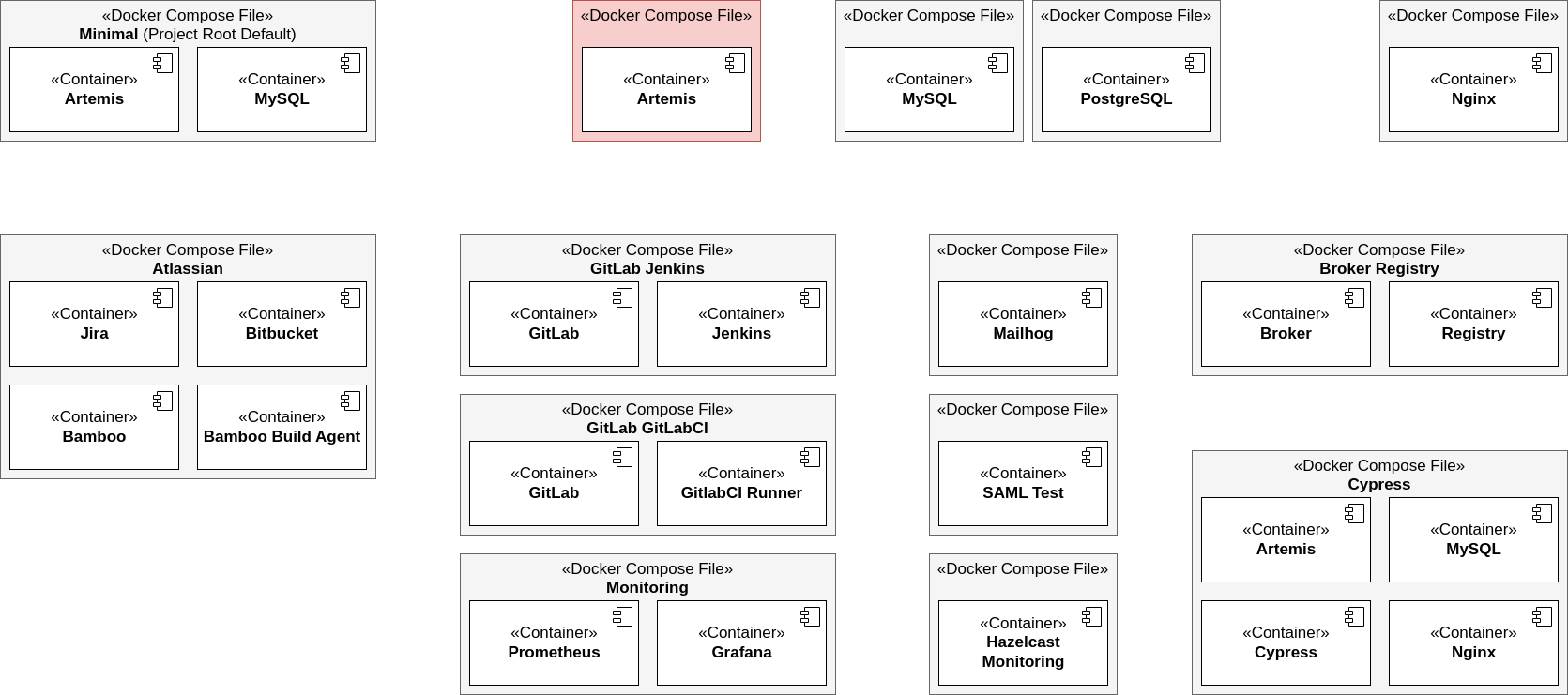
Overview of the Artemis Docker / Docker Compose structure
The easiest way to configure a local deployment via Docker is a deployment with a docker compose file.
In the directory docker/ you can find the following docker compose files for different setups:
artemis-dev-mysql.yml: Artemis-Dev-MySQL Setup containing the development build of Artemis and a MySQL DBartemis-dev-postgres.yml: Artemis-Dev-Postgres Setup containing the development build of Artemis and a PostgreSQL DBartemis-prod-mysql.yml: Artemis-Prod-MySQL Setup containing the production build of Artemis and a MySQL DBartemis-prod-postgres.yml: Artemis-Prod-Postgres Setup containing the production build of Artemis and a PostgreSQL DBgitlab-gitlabci.yml: GitLab-GitLabCI Setup containing a GitLab and GitLabCI instancegitlab-jenkins.yml: GitLab-Jenkins Setup containing a GitLab and Jenkins instance (see Gitlab Server Quickstart Guide for the configuration of this setup)monitoring.yml: Prometheus-Grafana Setup containing a Prometheus and Grafana instancemysql.yml: MySQL Setup containing a MySQL DB instancenginx.yml: Nginx Setup containing a preconfigured Nginx instancepostgres.yml: Postgres Setup containing a PostgreSQL DB instance
Three example commands to run such setups:
docker compose -f docker/atlassian.yml up
docker compose -f docker/mysql.yml -f docker/gitlab-jenkins.yml up
docker compose -f docker/artemis-dev-postgres.yml up
Tip
There is also a single docker-compose.yml in the directory docker/ which mirrors the setup of artemis-prod-mysql.yml.
This should provide a quick way, without manual changes necessary, for new contributors to startup an Artemis instance.
If the documentation just mentions to run docker compose without a -f <file.yml> argument, it’s
assumed you are running the command from the docker/ directory.
For each service being used in these docker compose files, a base service (containing similar settings) is defined in the following files:
artemis.yml: Artemis Servicemysql.yml: MySQL DB Servicenginx.yml: Nginx Servicepostgres.yml: PostgreSQL DB Servicegitlab.yml: GitLab Servicejenkins.yml: Jenkins Service
For testing mails or SAML logins, you can append the following services to any setup with an artemis container:
mailhog.yml: Mailhog Service (email testing tool)saml-test.yml: Saml-Test Service (SAML Test Identity Provider for testing SAML features)
An example command to run such an extended setup:
docker compose -f docker/artemis-dev-mysql.yml -f docker/mailhog.yml up
Warning
If you want to run multiple docker compose setups in parallel on one host, you might have to modify volume, container, and network names!
Folder structure
docker/.docker/<base service or setup name>/).Artemis Base Service
Everything related to the Docker Image of Artemis (built by the Dockerfile) can be found in the Server Setup section. All Artemis-related settings changed in Docker Compose files are described here.
artemis.yml base service (e.g. in the artemis-prod-mysql.yml setup) defaults to the latest
Artemis Docker Image tag in your local docker registry.docker compose build artemis-app before starting Artemis.image: value to the desired image
for the artemis-app service and run docker compose pull artemis-app.Debugging with Docker
See the Debugging with Docker section for detailed information.
In all development docker compose setups like artemis-dev-mysql.yml Java Remote Debugging is enabled by default.
Service, Container and Volume names
Service names for the usage within docker compose are kept short, like mysql, to make it easier
to use them in a CLI.
Container and volume names are prepended with artemis- in order to not interfere with other container or volume
names on your system.
Get a shell into the containers
Tip
To keep the documentation short, we will use the standard form of docker compose COMMAND from this point on.
You can use the following commands also with the -f docker/<setup to be launched>.yml argument pointing
to a specific setup.
app container:
docker compose exec artemis-app bashor if the container is not yet running:docker compose run --rm artemis-app bashmysql container:
docker compose exec mysql bashor directly into mysqldocker compose exec mysql mysql
Analog for other services.
Other useful commands
Start a setup in the background:
docker compose up -dStop and remove containers of a setup:
docker compose downStop, remove containers and volumes:
docker compose down -vRemove Artemis-related volumes/state:
docker volume rm artemis-data artemis-mysql-dataThis is helpful in setups where you just want to delete the state of artemis but not of Jenkins and GitLab for instance.
Stop a service:
docker compose stop <name of the service>(restart viadocker compose start <name of the service>)Restart a service:
docker compose restart <name of the service>Remove all local Docker containers:
docker container rm $(docker ps -a -q)Remove all local Artemis Docker images:
docker rmi $(docker images --filter=reference="ghcr.io/ls1intum/artemis:*" -q)