System Design
Top-Level Design
The following diagram shows the top-level design of Artemis which is decomposed into an application client (running as Angular web app in the browser) and an application server (based on Spring Boot). For programming exercises, the application server connects to a version control system (VCS) and a continuous integration system (CIS). Authentication is handled by an external user management system (UMS).
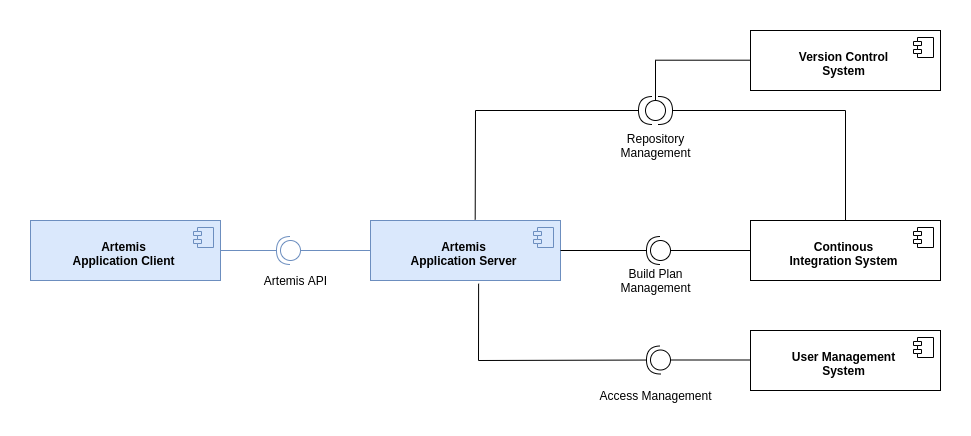
Top-Level Design
While Artemis includes generic adapters to these three external systems with a defined protocol that can be instantiated to connect to any VCS, CIS or UMS, it also provides 3 concrete implementations for these adapters to connect to:
VCS: Atlassian Bitbucket Server
CIS: Atlassian Bamboo Server
UMS: Atlassian JIRA Server (more specifically Atlassian Crowd on the JIRA Server)
Deployment
The following UML deployment diagram shows a typical deployment of Artemis application server and application client. Student, Instructor and Teaching Assistant (TA) computers are all equipped equally with the Artemis application client being displayed in the browser.
The Continuous Integration Server typically delegates the build jobs to local build agents within the university infrastructure or to remote build agents, e.g. hosted in the Amazon Cloud (AWS).
Deployment Overview
Data Model
The Artemis application server uses the following (simplified) data model in the MySQL database. It supports multiple courses with multiple exercises. Each student in the participating student group can participate in the exercise by clicking the Start Exercise button. Then a repository and a build plan for the student (User) will be created and configured. The initialization state helps to track the progress of this complex operation and allows recovering from errors. A student can submit multiple solutions by committing and pushing the source code changes to a given example code into the version control system or using the user interface. The continuous integration server automatically tests each submission, and notifies the Artemis application server, when a new result exists. In addition, teaching assistants can assess student solutions and “manually” create results.
Data Model
Please note, that the actual database model is more complex. The UML class diagram above omits some details for readability (e.g. lectures, student questions, exercise details, static code analysis, quiz questions, exam sessions, submission subclasses, etc.)
Server Architecture
The following UML component diagram shows more details of the Artemis application server architecture and its REST interfaces to the application client.
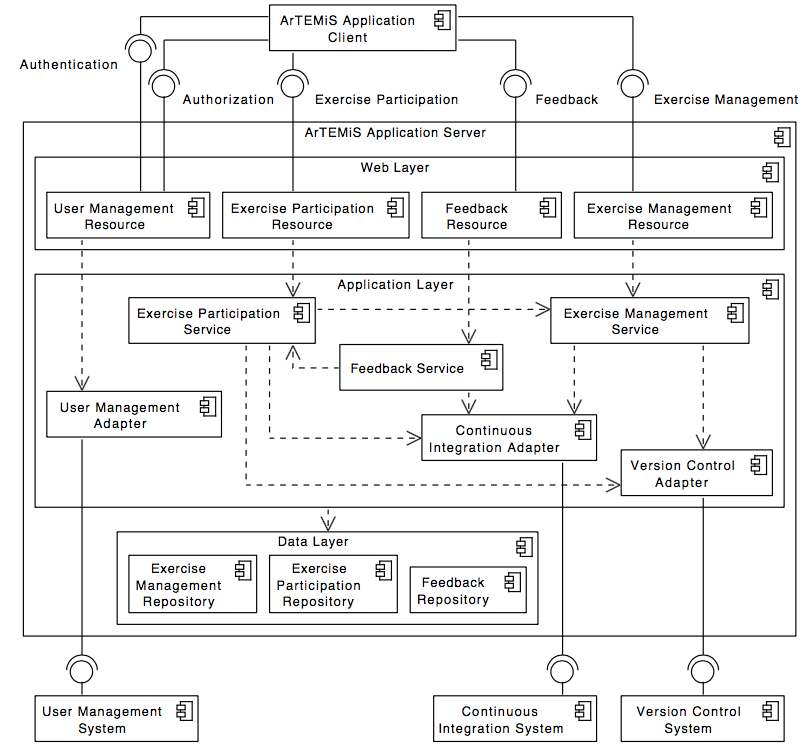
Server Architecture
Integrated Code Lifecycle
Artemis supports an integrated version control system (VCS) and continuous integration system (CIS). If you use Integrated Code Lifecycle, the architecture differs from the architecture with external VC and CI systems. An exemplary deployment with Integrated Code Lifecycle (without using an external user management system), consisting of one main application server and three build agent servers, looks like this:
Integrated Code Lifecycle Deployment
Employing the Integrated Code Lifecycle, administrators and developers can set the Artemis application up without the need for dedicated VCS and CIS installations. This new architecture simplifies the setup process, reduces dependencies on external systems, and streamlines maintenance for both developers and administrators. Developers have fewer applications to run in parallel, which translates into decreased system requirements. See Integrated Code Lifecycle Setup on how to set up a single-node environment for developing purposes. TODO: Additional reference to the production setup.
Version Control Subsystem
The following diagram shows an overview of the components in the version control subsystem:
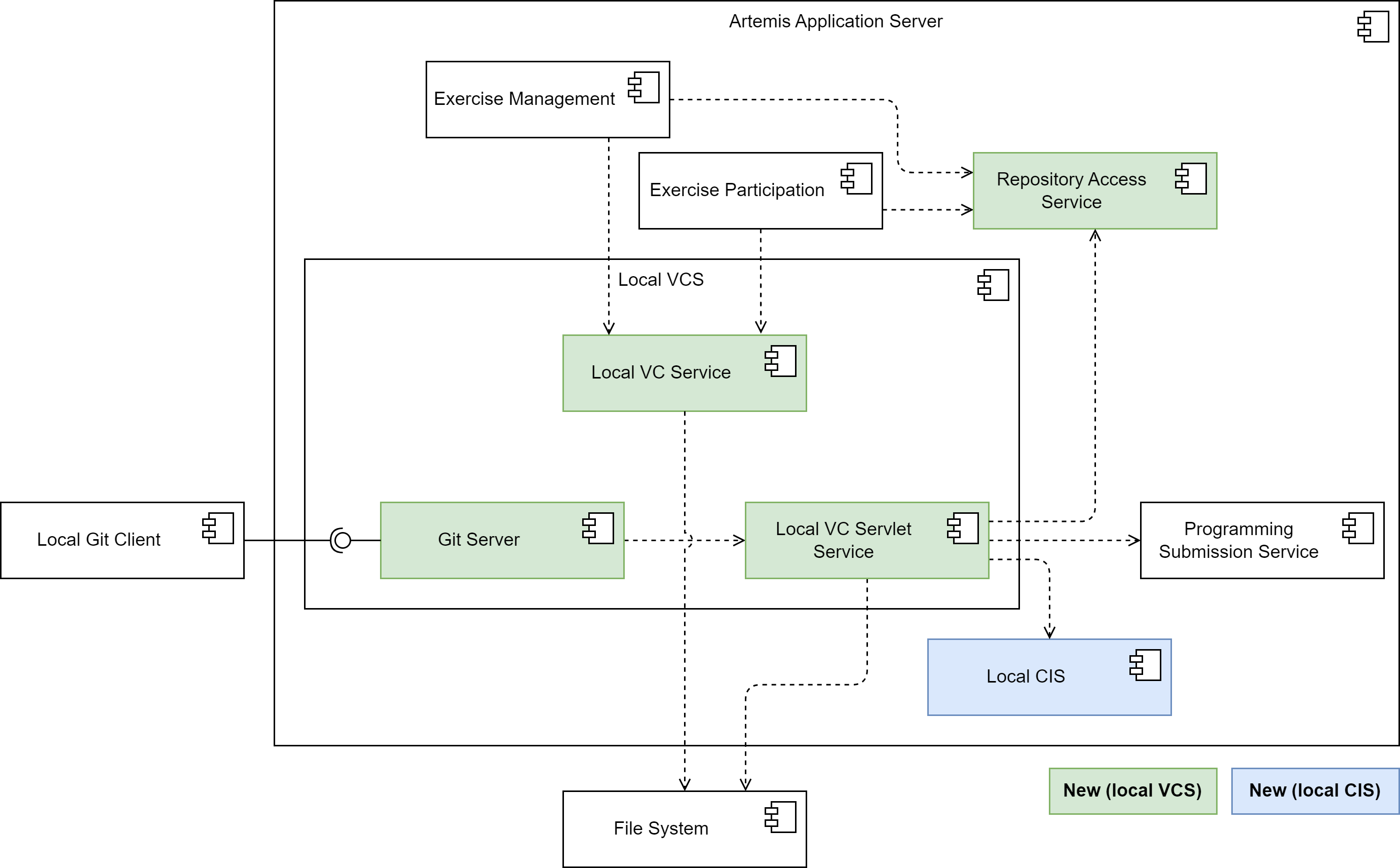
Version Control Subsystem
The Local VC Service implements the VersionControlService interface and thus contains methods that the exercise management subsystem and the exercise participation subsystem need to interact with the VC system.
E.g. the createRepository() method creates a repository on the file system.
For users to be able to access the repositories using their integrated Git client, the integrated VC subsystem contains a Git Server component.
It responds to fetch and push requests from Git clients, enabling instructors and students to interact with their repositories the way they are used to.
It encompasses all the logic for implementing the Git HTTP protocol server-side.
This includes extracting the command and parameters from the client request and executing the Git commands on the server-side repository, provided the repository exists, and the user has the requisite permissions.
It reads objects and refs from the repository, updates the repository for push requests, and formats the results of the Git commands it executes into a response that it sends back to the client.
This could involve sending objects and refs to the client in a packfile, or transmitting error messages.
The Git Server delegates all logic connected to Artemis to the Local VC Servlet Service.
This service resolves the repository from the file system depending on the repository URI. It also handles user authentication (only Basic Auth for now) and authorization.
For authorization (e.g. “is the requesting user the owner of the repository?”, “has the due date already passed?”), it uses the logic outsourced to the RepositoryAccessService that the existing online editor also uses.
For push requests, the Local VC Servlet Service calls the processNewProgrammingSubmission() method of the Programming Submission Service to create a new submission and finally calls the integrated CI subsystem to trigger a new build.
Integrating the VC system into the Artemis server application improves performance. For instance, when an instructor creates a new programming exercise, Artemis needs to copy the template source code to the template repository. Using the integrated VCS, Artemis merely needs to communicate with the host file system, copying the files from one location in the file system to another, which is faster than communicating with the external VCS through the network.
Continuous Integration Subsystem
The following diagram shows an overview of the components in the integrated continuous integration subsystem:
Continuous Integration Subsystem
The integrated CIS consists of two further subsystems: the CI Management and the Build Agent. Both systems are decoupled and can be deployed on separate servers if necessary (not obligatory). This allows for a flexible scaling of the system, as we can deploy multiple build agent instances to handle a high number of build jobs.
CI Management
The following diagram shows an overview of the components in the CI Management subsystem:
CI Management Subsystem
The CI Management prepares information for build jobs and add them to the distributed Hazelcast queue. It has complete access to the distributed data structures related to the CI system. It provides endpoints so users can interact with these datastructures, such as viewing and cancelling build jobs. It also receives the build job results, grades them, and notifies the user. The CI Management has access to the database and the file system.
The CI Management subsystem implements the ContinuousIntegrationTriggerService interface, the LocalCITriggerService which provides the triggerBuild method. This method gets called whenever a repository needs to be tested, i.e. after creating a programming exercise or when a student submits code.
When the triggerBuild method is called, all necessary information necessary to execute the build job is prepared and used to create a LocalCIBuildJobQueueItem object. The object contains, among other things, repository URIs, the build configuration, a user-defined build script (prepared by the LocalCIScriptService) and a priority value.
This object is then added to the job queue where it will then be retrieved by a build agent to execute the build job. The following diagram shows the structure of the LocalCIBuildJobQueueItem:
LocalCIBuildJobQueueItem
The CI Management subsystem consists of two additional services: The SharedQueueManagementService and the Local CI Result Processing Service.
The SharedQueueManagementService has direct access to the job queue as well as to other Hazelcast data structures, a map for currently running build jobs, a map for build agent information and a topic for cancelled build jobs.
The service provides the functionality for an Artemis user to interact with build jobs and build agents. Build jobs can be viewed and cancelled. Build agents can only be viewed at the current state of this thesis.
The user can access this functionality using the UI over a set of endpoints provided by a REST API.
The LocalCIResultProcessingService retrieves the build job results which were generated by the build agents from the result queue. It is responsible for grading the build job results, notifying the user and persisting information on the build job execution in the database.
Build Agent
The following diagram shows an overview of the components in the Build Agent subsystem:
Build Agent Subsystem
The build agent is a separate subsystem that is responsible for executing build jobs. It can be run as a standalone application or as part of the main Artemis application. The build agent implements multiple services responsible for retrieving queued build jobs and executing them.
The SharedQueueProcessingService has direct access to the job queue and detects newly added build jobs. The job is then taken from the queue if the build agent currently has the capacity to execute the job.
The service then makes an asynchronous method call to the BuildJobManagementService that eventually results in either a LocalCIBuildJobResult or an exception if something went wrong during the build job processing.
Either way, a ResultQueueItem object containing all necessary information about the build job execution is created and added to the result queue.
The BuildJobManagementService contains the logic for managing build jobs.
It prepares a build task in form of a lambda function and submits this task to the ExecutorService.
The ExecutorService encapsulates the low level logic for handling of the queue and the concurrency when running multiple build jobs on the build agent at a time.
As soon as a build job finishes, the ExecutorService returns the result of the task execution to the BuildJobManagementService.
The ExecutorService makes sure that errors happening during the build job execution are propagated to the BuildJobManagementService, so it can handle all errors in one spot.
To improve the reliability of the system, the BuildJobManagementService implements a timeout mechanism.
Administrators can configure a maximum amount of time that build jobs can run by setting the artemis.continuous-integration.timeout-seconds environment variable. The default value is 120 seconds.
If a build job times out, the BuildJobManagementService interrupts the build job.
This is crucial to prevent jobs that require an abnormally high amount of time from clogging up the system and reducing overall system performance.
The BuildJobExecutionService has the method runBuildJob, that contains the actual logic for executing a build job.
A basic build job for the purpose of providing automated assessment in Artemis consists of the following steps:
Check out the relevant repositories.
Configure Docker container.
Start a Docker container for the build job.
Copy repositories into container
Execute the build script in the container.
Retrieve the test results from the container.
Stop the container.
Parse the test results.
To address potential security risks associated with executing student code during automated assessment, we run the build job in a container, that the BuildJobContainerService creates and starts just for this purpose.
This container functions as an isolated environment.
If a student submits potentially malicious code, the container confines its execution, preventing it from directly affecting the host system or other containers.
The ephemeral nature of Docker containers allows the BuildJobExecutionService to quickly remove them and the data they produced during the build when a build job finishes.
Finally, when the build ran through successfully, the SharedQueueProcessingService puts the build result into the result queue so it can then be processed by the CI Management.
If there were any errors, the BuildJobManagementService stops the Docker container and SharedQueueProcessingService relays the exception message to the CI Management via the result queue.